Overview
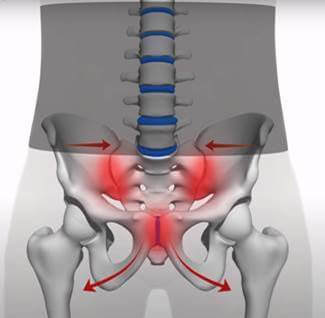
The importance of using the Serola Sacroiliac Belt during and, especially, after pregnancy cannot be overemphasized. During pregnancy, the ligaments, under hormonal influences, become lax and stretch to allow the pelvis to spread for delivery. It is important to hold the sacroiliac and pubic joints firmly together after delivery in order to assist the ligaments in shortening and realigning the pelvis properly. If you are looking for relief from hip pain, pelvic pain, and SI joint pain in pregnancy, a pregnancy SI belt will help.
Existing Studies Using a Pregnancy SI Belt
“Dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint was found in two-thirds of the women with severe back pain. This is important because dysfunction of the sacroiliac joints should be treated differently from other causes of low back pain. Backache tended to remain a problem after delivery among two-thirds of the women with severe pain during pregnancy. In some women, the pain persisted at least a year after the delivery. Most women treated with the trochanteric belt reported good results.” (Fast, et al. 1990) A trochanteric belt is the same as a sacroiliac belt.
In a study of 407 pregnant women, Ostgaard, et al. demonstrated a reduction of posterior pelvic pain in 82% of the women with the use of a non-elastic sacroiliac belt, especially while walking. They stated that “The use of a low non-elastic sacroiliac belt was a cost-effective unharmful tool for pain relief in many women with posterior pelvic pain.” (Ostgaard 1994) Because no side effects were found, they recommended the use of non-elastic sacroiliac belts for pregnant women who experienced posterior pelvic pain.
In a study of 862 women during pregnancy, Berg, et al. found that “49% experienced backache and one-third of these women considered the backache severe…The most common reason for severe low back pain was the dysfunction of the sacroiliac joints…and 79 women developed such severe pain that they were unable to continue work… Of these 79 women with severe pain, 72% experienced relief with a trochanteric (sacroiliac) belt.” (Berg, 1988)
Menstruation may make SIJ stabilization more difficult to acquire and maintain. DonTigny states “The presence of relaxin in the body about a week or 10 days before the onset of menstruation effects a hormonal ligamentous laxity similar to that of pregnancy but to a lesser degree and renders the pelvic ligaments less stable and more prone to a minor injury. The relaxin is reabsorbed during menstruation and if the innominate is kept in its normal position on the sacrum at this time, the pelvic ligaments seem to regain their normal stability. I have observed that if the dysfunction is not corrected, the instability may continue into the next menstrual cycle.” (DonTigny, 1985) It would seem appropriate then since a proper sacroiliac belt can help stabilize the sacroiliac joint and relieve SI joint pain, its use during menstruation would be beneficial.
Nilsson-Wikmar et al. divided 118 pregnant women into three groups, one with only a pelvic belt and an informational brochure on their condition with no exercise program. The other two groups were given different types of exercise programs, in addition to the belt and brochure. All women were tested at week 38 of pregnancy and 3, 6, and 12 weeks postpartum. They state that “At the three-month follow-up, 57% in group 1 and 35% in group 2 and 3 were pain-free…In conclusion, pelvic pain diagnosed during pregnancy seems to improve with time in all three different treatment groups.” (Nilsson-Wikmar, 1998) However, it should be noted that the group with only the belt and informational brochure benefited the most.
References:
Fast, A., et al., Low-back pain in pregnancy. Abdominal muscles, sit-up performance, and back pain. Spine, 1990. 15(1): p. 28-30.
Ostgaard, H.C., et al., Reduction of back and posterior pelvic pain in pregnancy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1994. 19(8): p. 894-900.
Berg, G., et al., Low back pain during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol, 1988. 71(1): p. 71-5.
DonTigny, R.L., Function and pathomechanics of the sacroiliac joint. A review. Physical Therapy, 1985. 65(1): p. 35-44.
Nilsson-Wikmar, L., et al. Effects of Different Treatments on Pain and on Functional Activities in Pregnant Women with Pelvic Pain. in 3rd Interdisciplinary World Congress on Low Back and Pelvic Pain. 1998. Vienna, Austria.
Serola SI Belt Vs. Belly Band
Belly Band
- Increases risk of atrophy and other adverse effects by taking the place of muscles.
- Does not reduce muscle spasms.
- Worn on the belly, increasing pressure in the abdominal cavity.
- Belly support bands are bulky, hot, and typically worn over clothing.
- Tend to bunch up, ripple, and/or slip out of position.
- Offer a very limited amount of functionality and support.
- Does not increase muscle strength.
- No longer useful once the body has returned to its previous condition.
Serola SI Belt
- Increases core strength and mobility by taking the place of ligaments that become looser during pregnancy.
- Reduces muscle spasms.
- Worn low and snug around the hips to stabilize the sacroiliac joint (SIJ) and to reduce SI joint pain in pregnancy.
- The Serola Belt is discreet, breathable, hypoallergenic, and can be worn under clothing.
- The entire surface of the belt is non-slip and conforms to the body.
- Provides a solution for Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction and numerous other medical conditions.
- The Serola Belt increases strength throughout the body, especially the trunk, upper legs, and arms.
- The Serola Belt is adjustable and can be used for years to come for both pain relief and pain prevention.
For even more relevant information on this topic, please see our blog article
Types of Pain Relief
What is Hip Pain
The hip and sacroiliac joint are the center holding points for stability in the body. When there is an injury or sprain in the hips or pelvis it can translate to not only pain found directly in the hip but can radiate into the lower back or even as far away as the neck and legs. Hip pain commonly occurs when a ligament or ligaments in the pelvic region have been stressed, strained or even torn; this causes instability in the pelvis and hip. The muscles then tighten to act as secondary stabilizers, which results in pain, discomfort and limited mobility. Pain may occur within the muscles and at their attachments to bone.
How does the Serola Sacroiliac Belt offer hip pain help?
Hip pain can be extremely distressing and cause issues with your quality of life. The Serola Sacroiliac Belt acts as an external ligament holding the joint in a normal range of motion. When the joint is placed into the “Normal Range” the muscles that are constantly tightening or turning on are able to relax. With the belt holding the body stable the pain being caused by constant muscle contraction is significantly reduced, if not completely gone. The belt should always be worn during any strenuous activity that involves lifting, bending, or twisting. Wearing the Serola Sacroiliac Belt will greatly reduce your chances of being injured or further injuring your body. This will help you avoid having to deal with issues such as hip pain, back pain, or sciatic hip pain.
